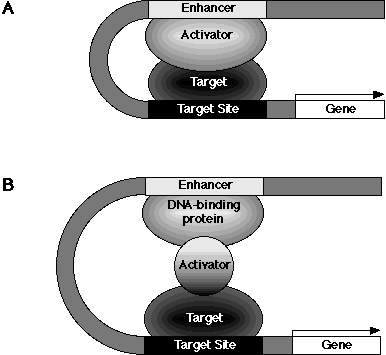
Figure 1.1. Model of gene activation by enhancers (based upon Fig. 1 of Ptashne and Gann (1990)).
The simplest model (A) involves an activator which has both a DNA-binding domain and an activating domain. The activator bound to its cognate DNA site, brings the target to the target's DNA site and/or activates the target's DNA-binding domain. The target then binds its cognate DNA site, which is located near the 5' end of the gene, and initiates transcription. The intervening DNA must thus loop out to accommodate this reaction. This scheme can easily be extended to more complex arrangments (B) where the activating domain lies in a separate factor which must bind a protein which recognises the enhancer sequence. This arrangment can be extended to involve any number of intermediate factors between the enhancer sequence and the target site.

