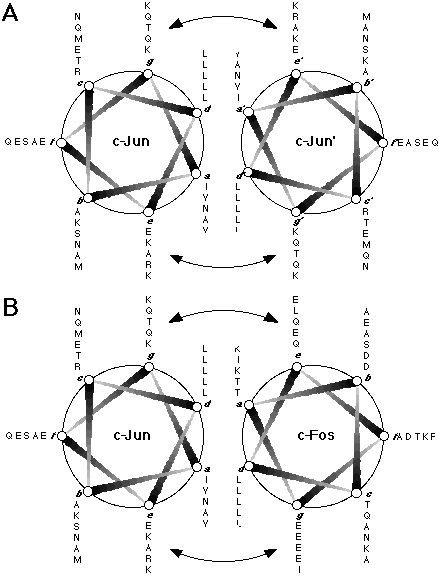
Figure 1.5. Helical wheel representations of c-Jun and c-Fos.
(A) The c-Jun homodimer and (B) the c-Jun:c-Fos heterodimer interacting as in a coiled-coil structure; the sequences plotted comprise residues 277-315 of c-Jun and residues 162-200 of c-Fos. The coiled-coil consists of a heptad repeat of residues (labelled a to g), where residues a and d are generally hydrophobic and form the interface between the two helices. In leucine zipper proteins, the d position is generally occupied by a leucine or isoleucine residue, while the a position is most frequently occupied by the 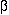 -branched residues isoleucine, threonine, or valine. The arrows indicate electrostatic interactions between residues at the e and g positions which are assumed to further stabilise the coiled-coil structure and regulate the specificity of the dimerisation.
-branched residues isoleucine, threonine, or valine. The arrows indicate electrostatic interactions between residues at the e and g positions which are assumed to further stabilise the coiled-coil structure and regulate the specificity of the dimerisation.

