The twenty amino acids found in biological systems are:
Proteins are very complicated moleucules. With 20 different amino acids that can be arranged in any order to make a polypeptide of up to thousands of amino acids long, their potential for variety is extraordinary. This variety allows proteins to function as exquisitely specific enzymes that compose a cell's metabolism. An E. coli bacterium, one of the most simple biological organisms, has over a 1000 different proteins working at various times to catalyze the necessary reactions to sustain life.
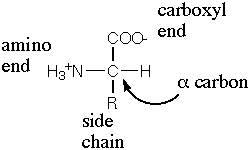
All amino acids have the same general formula:

The twenty amino acids found in biological systems are:
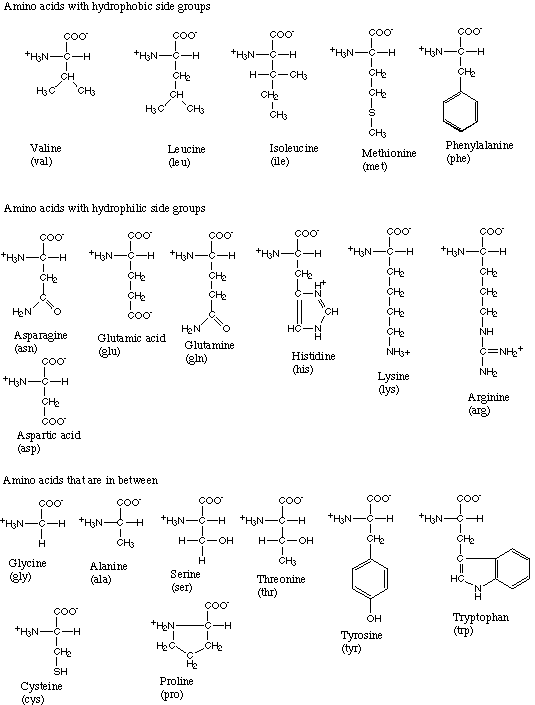
All proteins are linear chains composed of these 20 amino acids.