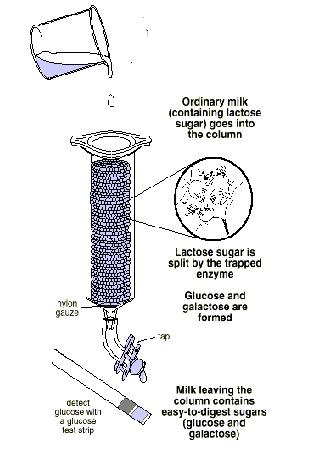
Lactase (or ?-galactosidase) is strongly
inhibited by galactose (one of the products of its action
on lactose). Hence the flow rate of the substrate over the column is critical
to the rate of the enzyme-catalysed reaction: too
fast and there isn't time for the reaction to occur; too slow a rate and
galactose will accumulate and then inhibit the reaction.
You can therefore investigate the effect of flow rate on the conversion
of lactose to glucose and galactose.
 1. Mix 2 ml of lactase
enzyme with 8 ml of
2% sodium alginate
1. Mix 2 ml of lactase
enzyme with 8 ml of
2% sodium alginate
solution
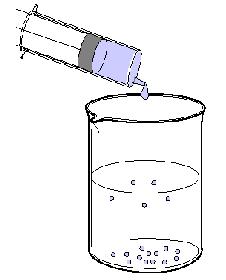
chloride solution a drop at a time
Allow the beads to
set for a few minutes
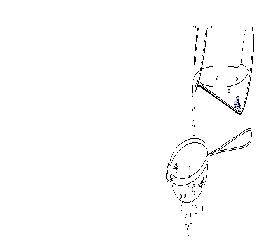
chloride solution
syringe barrel