lipases? Can boric acid be used to inhibit proteases and so overcome this problem?
2. Investigate the effect
of pH on the activity of the two enzymes.
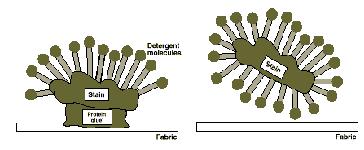
As well as attacking protein stains directly, enzymes
degrade the protein 'glue'
that sticks other stains to fabric, allowing detergents
to lift them free.
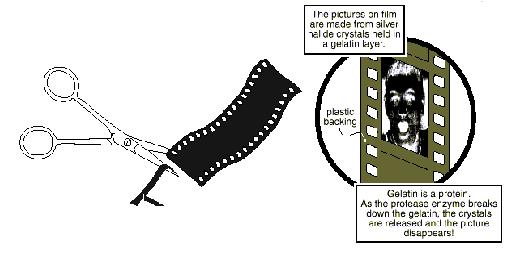
Gelatin is a protein. As the protease enzyme breaks down the gelatin, the crystals
are released and the picture disappears!

different types of protease enzyme to it.
(Use 1-2 g of enzyme for every
100 g of powder.)
negatives.
temperatures.

film. Which enzyme works best? What is the
best temperature
for your new product?