The NS1 protein (nonstructural protein 1) of the influenza A virus has
multiple post-transcriptional functions and RNA-binding activities. First,
by sepesifically binding polyA tails of mRNA, NS1 retains polyA-containing
mRNAs in the cell nucleus. Second, NS1 directly inhibits pre-mRNA splicing
by binding tightly to a sepesific stem-bulge region of the U6 snRNA. Third,
by binding to dsRNA, NS1 blocks the initiation of translation by both
cellular and viral mRNAs.
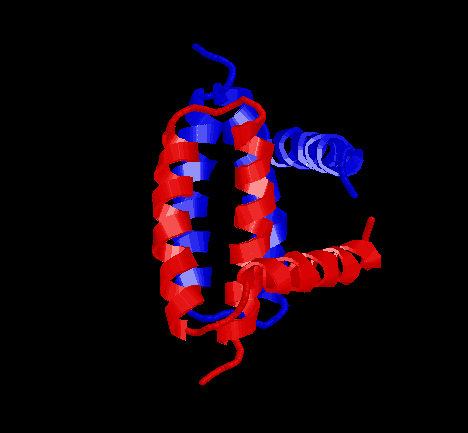
The NS1 protein exists as dimer. The RNA binding domain of the NS1
protein is at the N-terminal, containing the first 73 residues. This domain
has threeŁ\helices in the secondary structure of NS1. In dimer, the six
helical fold does not match any other known RNA-binding protein.
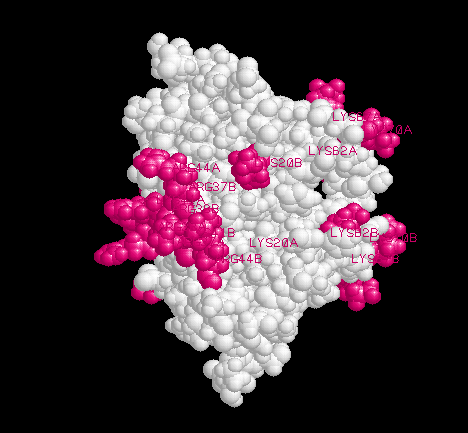
Different RNA-binding activities of NS1 may map to different epitopes
on the surface of the domain. Only structural studies of NS1-RNA complexes
can give a definitive picture of how NS1 binds to RNA.