Purpose: Fine QTL (quantitative trait locus) Mapping
¡@
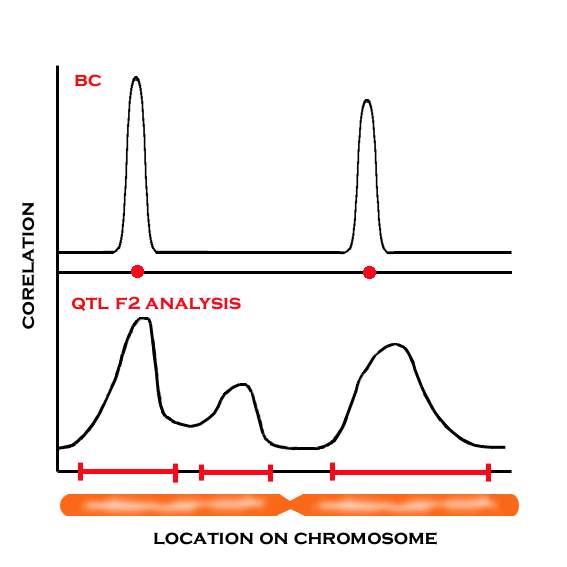
General QTL F2 Analysis:
F2 continuous series of morphologies
Assess for their quantitative phenotype, and estimate made of the contribution (or lack of contribution) of specific segment to the observed variation.
The average phenotype of lines with region A is compared with the average of lines lacking region A. If there is a difference, region A becomes a candidate to contain a QTL.
¡@
Mapping is possible with the help of a lot of molecular markers.
Such as RFLP (restriction enzyme fragment polymorphism), SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism), or SSLP(short sequence length polymorphism).
¡@
Artificial Selection
If backcross to simulans, then select the genital arch phenotype like sechellia, and continue to backcross to simulans.
Thus, we can dilute the sechellia genome that is not correlated to genital arch morphology, then get a finer map of QTL mapping.
Artificial selection helps narrow down the region of mapping.
If the QTL is recessive ?