HOMEWORK#8
Sequence analysis
/ model building
-
David Liu, a student
in the department of Lfe Sciences, got a clone from E coli. Here
is the DNA sequence:
TGGATGCCATGTTCCGGAGGTAATATGAAGAAATCAATATTATTTATTTTTCTTT
CTGTATTGTCTTTTTCACCTTTCGCTCAGGATGCTAAACCAGTAGAGTCTTCAAA
AGAAAAAATCACACTAGAATCAAAAAAATGTAACATTGCAAAAAAAAGTAATA
AAAGTGGTCCTGAAAGCATGAATAGTAGCAATTACTGCTGTGAATTGTGTTGTA
ATCCTGCTTGTACCGGGTGCTATTAATAATATAAAGGGAACTAAACAGTTCCCT
TTATATTTGTTCTGATTCTGATGATGTCTGTAACGTATGTCCTGTTGCTTTGTTG
AATAAATCGA
Unfortunately,
he doesn't know how to use the sequence analysis tools availabled in the
internet since he did not take Bioinformatics course before. Could you
help him to do the following analysis?
-
(1) Find its corresponding
polypeptide sequence
(DNA -> Protein translation).
-
(2) Identify this
protein. Is it a new protein?
-
(3) Report the
total number of negatively charged residues and positively
charged residues.
-
(4) Color
the protein by its charge.
-
(5) Draw the hydrophobicity
map for this protein using Eisenberg hydrophobicity scale with window
size 7. The relative weight of the window edges compared to the window
center should set to 40%.
-
(6) Please help
him to use Prosite
scanning tool to find out possible functions or pattern
of this protein.
-
(7) Calculate
its pI
and molecular weight.
(1) Ans:
Number of amino acids: 72
Met K K S I L F I F L S V L S F S P F A Q D A K P
V E S S K E K I
T L E S K K C N I A K K S N K S G P E S Met N S S N YC C E L C
C N P A C T G C Y Stop
(2)
Ans:
Yes,it is a new protein.
Definition:E.coli heat-stable toxin (st) gene
Identities = 286/336 (85%), Positives = 286/336 (85%), Strand = Plus /
Plu
Query:1 TGGATGCCATGTTCCGGAGGTAATATGAAGAAATCAATATTATTTATTTTTCTTTCTGTA 60
Sbjct: 1 TGGATGCCATGTTCCGGAGGTAATATGAAGAAATCAATATTATTTATTTTTCTTTCTGTA
60
Query:61 TTGTCTTTTTCACCTTTCGCTCAGGATGCTAAACCAGTAGAGTCTTCNNNNNNNNNNNNN 120
Sbjct: 61 TTGTCTTTTTCACCTTTCGCTCAGGATGCTAAACCAGTAGAGTCTTCAAAAGAAAAAATC
120
Query:121 NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNGTAATAAAAGTGGTCCTGAAAGC
180
Sbjct: 121 ACACTAGAATCAAAAAAATGTAACATTGCAAAAAAAAGTAATAAAAGTGGTCCTGAAAGC
180
Query:181 ATGAATAGTAGCAATTACTGCTGTGAATTGTGTTGTAATCCTGCTTGTACCGGGTGCTAT
240
Sbjct: 181 ATGAATAGTAGCAATTACTGCTGTGAATTGTGTTGTAATCCTGCTTGTACCGGGTGCTAT
240
Query: 241 TAATAATATAAAGGGAACTAAACAGTTCCCTTTATATTTGTTCTGATTCTGATGATGTCT
300
Sbjct: 241 TAATAATATAAAGGGAACTAAACAGTTCCCTTTATATTTGTTCTGATTCTGATGATGTCT
300
Query:301 GTAACGTATGTCCTGTTGCTTTGTTGAATAAATCGA 336
Sbjct: 301 GTAACGTATGTCCTGTTGCTTTGTTGAATAAATCGA
336
Minus Strand HSPs:Score = 134 (37.0 bits), Expect = 0.46, P = 0.37
Identities = 30/34 (88%), Positives = 30/34 (88%), Strand = Minus / Plus
Query: 278 AATATAAAGGGAACTGTTTAGTTCCCTTTATATT 245
Sbjct: 245 AATATAAAGGGAACTAAACAGTTCCCTTTATATT 278
Function:Toxin which activates the particulate
from of guanylate cyclase and increases cyclic GMP levels
within the host intestinal epithelial cells.
Disease: Both heat-stable and heat-labile
enterotoxins are produced by pathogenic strains of E.coli and
effect the digestive tract of mammals.
SIGNAL 1
19 BY SIMILARITY.
PROPEP 20 53
BY SIMILARITY.
PEPTIDE 54
72 ENTEROTOXIN A4.
DISULFID 59 64
BY SIMILARITY.
DISULFID 60
68 BY SIMILARITY.
DISULFID 63 71
BY SIMILARITY
M K K S I L F I F L S V L S F S P F A Q
D A K P V E S S K E K I T L E S K K C N I A K K S N K S G P E S M
N S S N YC C E L C C N P A C T G C Y
|_|____
|_|
|
|
|____ |________|
|
|_____________|
(3)
Ans:
Total number of negatively charged residues
(Asp + Glu): 6
Total number of positively charged
residues (Arg + Lys): 10
(4) Ans:
negatively charged : D,E ( Red
)
positively charged: R,K ( Blue
)
Met K K S I L
F I F L S V L S F S P F A Q D
A K P V E
S S K E
K I T
L E S K
K C N I A K K
S N K S
G P E S Met N
S S N YC C E
L C C N
P A C T G C Y Stop
(5)
Ans:
Using the scale Hphob. / Eisenberg et al., the individual values for the
20 amino acids are:
|
Ala
|
Arg
|
Asn
|
Asp
|
Cys
|
Gln
|
Glu
|
Gly
|
His
|
Ile
|
Leu
|
Xaa
|
|
0.620
|
-2.530
|
-0.78
|
-0.900
|
0.290
|
-0.850
|
-0.740
|
0.480
|
-0.400
|
1.380
|
1.060
|
-0.000
|
|
Lys
|
Met
|
Phe
|
Pro
|
Ser
|
Thr
|
Trp
|
Tyr
|
Val
|
Asx
|
Glx
|
|
|
-1.500
|
0.640
|
1.190
|
0.120
|
-0.180
|
-0.050
|
0.810
|
0.260
|
1.080
|
-0.840
|
-0.795
|
|
Weights for window positions 1,..,7,
using linear weight variation model:
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
|
0.40
|
0.60
|
0.80
|
1.00
|
0.80
|
0.60
|
0.40
|
|
edge
|
|
|
center
|
|
|
edge
|
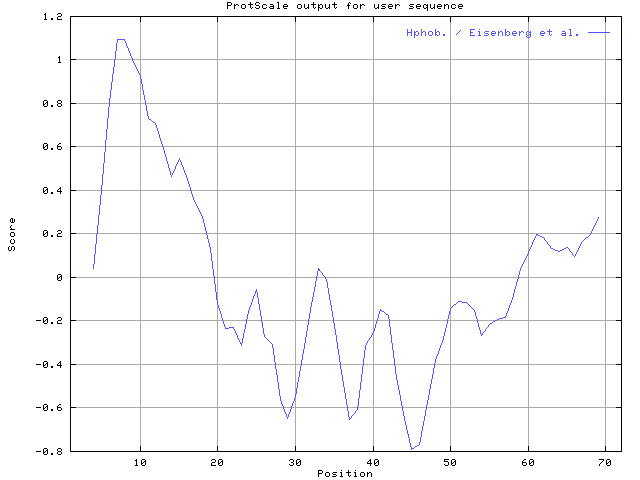
(6)
Ans:
-
This pattern is
found in most of the known physiological substrates.
It has been
known for a long time that potential N-glycosylation sites are
specific to
the consensus sequence Asn-Xaa-Ser/Thr. It must be noted that the
presence of
the consensus tripeptide is not sufficient to conclude
that an
asparagine
residue is glycosylated, due to the fact that the folding of
the
protein plays
an important role in the regulation of N-glycosylation . It
has been shown
that the presence of proline between Asn and Ser/Thr will
inhibit N-glycosylation;
this has been confirmed by a recent statistical
analysis of
glycosylation sites, which also shows that about 50% of the sites
that have
a proline C-terminal to Ser/Thr are not glycosylated.
It must also
be noted that there are a few reported cases of glycosylation
sites with
the pattern Asn-Xaa-Cys; an experimentally demonstrated occurrence
of such a
non-standard site is found in the plasma protein C .
-Consensus
pattern: N-{P}-[ST]-{P} (N is the glycosylation
site)
-
Number of matches:
2
1: 46-49 NKSG
2 : 54-57 NSSN
-
Protein kinase
C phosphorylation site
-
In vivo, protein
kinase C exhibits a preference for the phosphorylation
of
serine or threonine residues found close to a C-terminal basic residue
[1,2].
The presence of additional basic residues at the
N- or C-terminal of the
target amino acid enhances the Vmax and Km of the phosphorylation reaction.
-Consensus pattern: [ST]-x-[RK] (S or T is the phosphorylation site)
1: 27-29 SSK
2 : 36-38 SKK
3 : 45-47 SNK
-
Casein kinase
II phosphorylation site
-
Casein kinase
II (CK-2) is a protein serine/threonine kinase whose activity is
independent of cyclic nucleotides and calcium.
CK-2 phosphorylates many
different proteins. The substrate specificity [1]
of this enzyme can be
summarized as follows:
(1) Under comparable conditions Ser is favored over Thr.
(2) An acidic residue (either Asp or Glu) must be present three residues
from
the C-terminal of the phosphate acceptor site.
(3) Additional acidic residues in positions +1, +2, +4, and
+5 increase the
phosphorylation rate. Most physiological substrates
have at least one
acidic residue in these positions.
(4) Asp is preferred to Glu as the provider of acidic determinants.
(5) A basic residue at the N-terminal of the acceptor
site decreases the
phosphorylation rate, while an acidic one will increase it.
-Consensus pattern: [ST]-x(2)-[DE] (S or T is the phosphorylation site)
1: 27-30 SSKE
2: 48-51 SGPE
-
Heat-stable enterotoxins
signature
-
Prokaryotic heat-stable
enterotoxins [1] are responsible for acute diarrhea.
The active toxin is a short peptide of around twenty residues
which contains
six cysteines
involved in three disulfide bonds, as shown in
the following
schematic
representation:
xxCCxxCCxxxCxxCxx
'C':
conserved cysteine involved in a disulfide bond.
We have
taken the pattern of cysteines, along with three conserved residues,
as a signature
pattern for this group of proteins.
-Consensus
pattern: C-C-x(2)-C-C-x-P-A-C-x-G-C[The six C's are involved in disulfide
bonds]
(7) Ans:
Molecular weight: 7909.2
Theoretical pI: 8.72

