
![]() Forming
a complex with calcium and phospholipid headgroups.
Forming
a complex with calcium and phospholipid headgroups.
Calcium ions mediate interactions with the phospholipid headgroups,
creating a charge-charge interaction.
![]() Burying
highly exposed large hydrophobic residues.
Burying
highly exposed large hydrophobic residues.
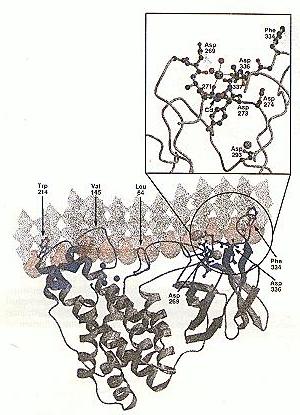
The plane defined by two extremely expose hydrophobic residues
Trp 214 and Phe 334 , indicates the approximate position
of a membrane binding surface.
![]() A
highly hydrophobic, disordered surface loop (residues 84-88).
A
highly hydrophobic, disordered surface loop (residues 84-88).
a. Phospholipid taigroup binding.
b. Communicating calcium and/or membrane-binding to the active site,
thereby initiating any conformational changes required to activate
enzyme.