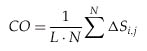
where N is the total number of contacts, ![]() Si,j
is the sequence separation, in residues, between contacting residues i
and j, and L is the total number of residues in the protein.
Si,j
is the sequence separation, in residues, between contacting residues i
and j, and L is the total number of residues in the protein.
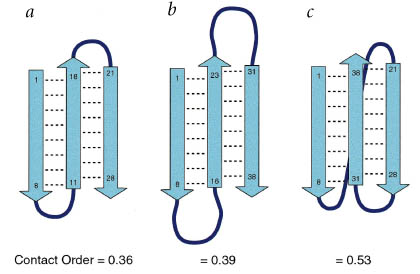
Contact Order Parameter |
| Definiton of Relative Contact Order (CO) |  |
| Relative contact order is the average sequence distance between all pairs of contacting residues normalized by the total sequence length: | |
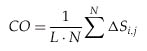 |
|
|
where N is the total number of contacts, |
|
| Contact order is related to secondary structural content. Yet, helices are characterized by numerous i, i+3 contacts orders of helical proteins tend to be low and thus there is a significant correlation between contact order and helical content (r = 0.72; p = 0.009). This suggests that contact order is a important determinant of protein folding kinetics. | |
Ab initio by ROSETTA |
Theoretical analysis of SH3 folding. a, Ab initio simulation of src SH3 folding using ROSETTA. All SH3 domain structures were removed from the data base of short fragments used for building up conforma-tions. A total of 500 independent simulations were carried out, and all conformations from the 20 trajectories that produced structures within 4.5 A r.m.s.d. of the native structure were combined to calculate the frequency of side chainíVside chain contacts for each pair of residues in the protein (lower right triangle; color scheme is shown below the figure). For comparison, the contact distribution in the native structure is shown in the upper left. b, Hierarchy of SH3 domain folding in model calculations based on native state topology. Calculations were performed on the src, spectrin and fyn SH3 domains and the 47íV48 circular permutant of the spectrin SH3 domain in which the distal hairpin has been cut. The reaction coordinate, Nf, is the fraction of ordered residues (Nf = 0 is the fully unfolded state and Nf = 1 is the fully folded state). The y-axis indicates position along the sequence. All configurations of the system were enumerated, and the Boltzmann averaged frequency of ordering of each residue, as a function of Nf, is indicated by the color (black-blue, 0íV0.25; blue-magenta, 0.25íV0.50; magenta-red, 0.50íV0.75; red-yellow, 0.75íV0.88; and yellow-white, 0.88íV1.00). It is important to note that segments of the protein not contiguous along the sequence still interact in the model if contacting in the three-dimensional structure, for example in the top panel, the high population of the diverging turn/strand 2 and the distal loop b-hairpin at Nf = 0.6 indicates that more surface area is buried within and between these structural elements than within any other substructure with the same number of residues ordered in the protein. (Figure adopted from Riddle et al., Nat. Struct. Biol., 1999, 6(11):1016) |
3a.gif) |
|
3b.gif) |
Danny S. Hsu 1999-2000. All rights reserved.