Gas gangrene
Gallery

![]()
Table Of Contents:
Alternative names
Definition
Causes, incidence,
and risk factors
Prevention
Symptoms
Signs and tests
Treatment
Expectations (prognosis)
Complications
Calling your health care
provider
![]()
Alternative names:
tissue infection - clostridial; gangrene - gas; clostridial infection
of tissues; clostridial myonecrosis
![]()
Definition:
A severe form of gangrene (tissue death) caused by Clostridium perfringes
(see also necrotizing
subcutaneous infection).
![]()
Causes,
incidence, and risk factors:
Gas gangrene occurs as a result of infection by Clostridium species
of bacteria that under anaerobic
(low oxygen) conditions, produce toxins
that cause the tissue death and associated symptoms.
Gas gangrene generally occurs at the site of trauma or a recent surgical wound. The onset of gas gangrene is sudden and dramatic. Inflammation begins at the site of infection as pale to brownish-red extremely painful tissue swelling. Gas may be felt in the tissue as a crackly sensation when the swollen area is pressed with the fingers. The margins of the infected area expand so rapidly that changes are visible over a few minutes of time. The involved tissue is completely destroyed.
Clostridia species of bacteria produce many different toxins, four of which (alpha, beta, epsilon, iota) are all fatal. In addition they cause tissue death (necrosis), destruction of blood (hemolysis), local decrease in circulation (vasoconstriction), and leaking on the blood vessels (increased vascular permeability). These toxins are responsible for both the local tissue destruction and the systemic symptoms (the other symptoms throughout the body).
Systemic symptoms develop early in the infection. These consist of sweating,
fever,
and anxiety.
If untreated the individual develops a shock
- like syndrome with decreased blood
pressure (hypotension),
renal
failure, coma,
and finally death.
![]()
Prevention:
Clean any skin injury thoroughly. Watch for signs of infection such
as redness, pain, drainage, or swelling
around the wound,
and consult the health care provider promptly if these occur.
- moderate to severe pain around a skin injury
- progressive swelling around a skin injury
- moderate to low fever
- skin color initially pale, later dusky to highly discolored
- skin color progressing to dark red or purple
- vesicle (blister) formation, coalescent (combine into large blisters)
- blisters filled with brown-red fluid
- drainage from the tissues, foul-smelling brown-red or bloody fluid (serosanguineous discharge)
- increased heart rate (tachycardia)
- sweating
- subcutaneous emphysema
![]()
Signs and tests:
Shock
may be present, as evidenced by general pallor,
cold extremities, low
blood pressure, and rapid
heart rate. Air in the tissues (crepitus)
may be felt. Infection involving the entire body (systemic
toxicity or sepsis)
may develop. Yellow
skin color associated with the excessive breakdown of blood cells (jaundice)
is possible.
- A gram stain of fluid from the infected area shows gram positive rods and spoke formation.
- An anaerobic tissue and/or fluid culture reveals Clostridium species.
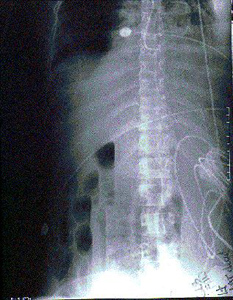
- An X-ray, CT scan, or MRI of the area shows gas in the tissues.
Treatment:
Prompt surgical removal of dead, damaged and infected tissue (debridement) is necessary. Amputation may be indicated to control the spread of infection.
Antibiotics, preferably penicillin-type, should be given. Initially, this is given intravenously (through a vein). Analgesics may be required to control pain.
Hyperbaric oxygen has been tried with varying degrees of success.
![]()
Expectations
(prognosis):
Gas gangrene is progressive and often lethal. Immediate medical attention
is required.
- disfiguring or disabling permanent tissue damage
- jaundice with liver damage
- kidney failure
- spread of infection systemically through the body (sepsis)
- shock
- stupor
- delirium
- coma
Calling your health care provider:
Call your heath care provider if signs of infection occur at any time around a skin wound; including pain, swelling, redness, drainage of pus or blood, fever, or similar symptoms.
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as
911) if symptoms indicate gas gangrene. This is an emergency condition
requiring immediate medical attention!
![]()
[Alternative names] [Definition]
[Causes, incidence, and
risk factors] [Prevention] [Symptoms]
[Signs and tests] [Treatment]
[Expectations (prognosis)] [Complications]
[Calling your health care
provider]
![]()
![]()
Copyright Notice: The information provided herein should
not be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed
physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all
medical conditions. (see disclaimer).
This HTML page and its contents ©1999 A.D.A.M.
Software, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained
herein is strictly prohibited.
