張大慈老師實驗室
Professor Dr. Margaret Dah-Tsyr Chang
Starch-Binding Domain (SBD)
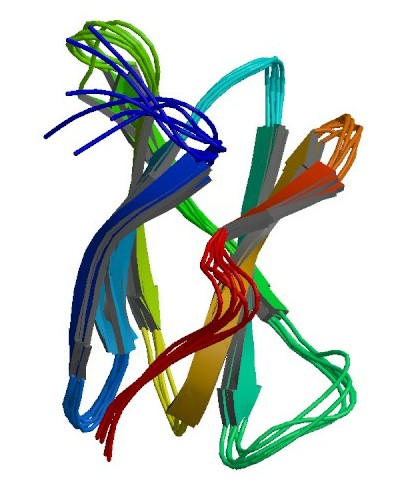
RoSBD belonging to CBM family 21 with a molecular weight of 11.7 kDa, and is classified as a member of Type B glycan chain-binding CBM. Ro-SBD consists of eight β-strands forming two β-sheets with a distorted barrel structure. RoSBD possesses two ligand-binding sites, where hydrophobic interactions between the sugar rings and aromatic residues on RoSBD surface play crucial roles in ligand binding. RoSBD has been demonstrated to be effectively adsorbed onto raw starch and other soluble oligosaccharides. The binding of RoSBD has been identified to be stable over a wide range of conditions; hence it can be eluted from starch or amylose resin with elevated pH. RoSBD has been developed as a rapid and economic recombinant protein purification system depending on pH.
Eosinophil Cationic Protein (ECP)

Eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) is secreted by activated granular eosinophilic leukocytes and is the best known protein marker for asthma and other inflammatory diseases. ECP belongs to human ribonuclease (RNase) A superfamily and is also named as RNase 3. It is a single polypeptide composed of 133 amino acids with three α-helices and six beta sheets. Our studies revealed that the cytotoxic activity of ECP toward Beas-2B human bronchial epithelial cells depended on binding to the cell surface glycosaminoglycan (GAGs), specifically heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs), followed by endocytosis. We have demonstrated the key residues in heparin binding motif for cell binding, and discovered multiple functions of ECP, which facilitates understanding of molecular interaction between ECP and cell surface and cell membrane components, as well as cytotoxicity mechanisms of ECP.

學歷
- 美國馬里蘭州約翰霍浦金斯大學化學系博士 (1993年)
- 美國馬里蘭州約翰霍浦金斯大學化學系碩士 (199l年)
- 國立臺灣大學化學系(l987年) 學士
經歷
- 國立清華大學分子與細胞生物研究所所長 (2011年-迄今)
- 國立清華大學分子與細胞生物研究所教授 (2007年-迄今)
- 英國牛津大學化學系訪問學者 (2011年)
- 國立清華大學研發處智財技轉組組長 (2008年-2011年)
- 國立清華大學生命科學系副教授 (1995年-2007年)
- 國立清華大學生命科學系專任講師 (l993-l995年)
- 美國馬里蘭州約翰霍浦金斯大學化學系兼任研究助理 (1990-1993年)
- 美國馬里蘭州約翰霍浦金斯大學化學系兼任助教 (1988-l990年)
- 國立臺灣大學化學系專任助教 (l987-l988年)
獲獎
- 2006
- 台北生技獎產學合作銀獎
- 國立清華大學95年教師學術卓越獎勵
- 2007
- 國立清華大學第一屆傑出產學合作獎
- 國科會績優技轉中心獎(第一次)
- 國立清華大學96年教師學術卓越獎勵
- 2008
- 國立清華大學生命科學院傑出研究獎
- 國科會績優技轉中心獎(第二次)
- 國立清華大學97年教師學術卓越獎勵
- 2009
- 國科會績優技轉中心獎(第三次)
- 國立清華大學98年教師學術卓越獎勵
- 2010
- 生策會國家新創獎(學術研究組)-澱粉結合蛋白之分子設計與應用
- 經濟部99年度大學產業經濟貢獻獎(團體組)
- 國科會績優技轉中心獎(第四次)
- 國立清華大學99年教師學術卓越獎勵
- 2011
- 國科會與英國頂尖大學合作前期計畫
- 國科會優秀年輕學者研究計畫
- 國立清華大學傑出學術研究出版獎勵
- 國立清華大學100年教師學術卓越獎勵
- 2012
- 國立清華大學傑出學術研究出版獎勵
